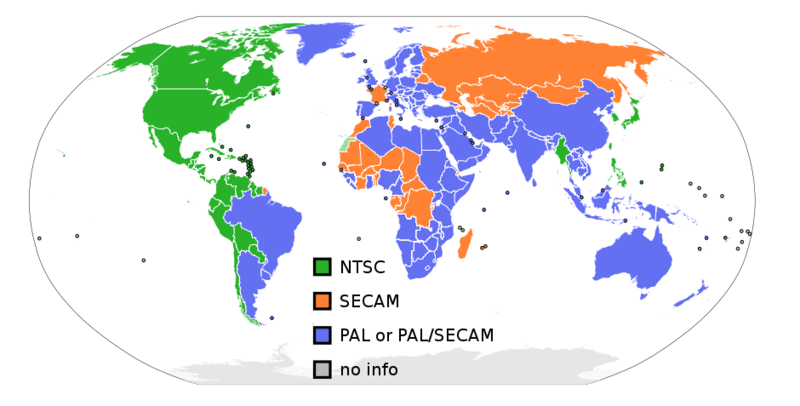
NTSC (National Television Standards Committee) and PAL (Phase Alternating Line) are two television encoding systems that are dominating the world at present. NTSC delivers a frame rate of 30 fps at an aspect ratio of 720x480, and is used in North America, Japan and South Korea. PAL is a different video standard that is incompatible with NTSC; it uses a fame rate of 25 fps and 720x576 aspect ratio, and is used in most of Europe, Australia and large parts of Africa and Asia. The differences between NTSC and PAL are the reason why some DVDs or VHS tapes from Europe may not play in the United States and vice versa. Most European DVD players can read NTSC and most PAL TVs can display NTSC video. But NTSC DVD players usually cannot read PAL.
There is a third standard, called SECAM (Sequential Couleur Avec Memoire or Sequential Color with Memory), that is used in Eastern Europe and France.
Comparison chart
NTSC |
PAL |
|
| Abbreviation | National Television System Committee | Phase Alternation by Line |
| Video Bandwidth | 4.2 MHz | 5.0 MHz |
| Sound Carrier | 4.5 MHz | 5.5 MHz |
| Bandwidth | 6 MHz | 7 to 8 MHz |
| Vertical Frequency | 60 Hz | 50 Hz |
| Horizontal Frequency | 15.734 kHz | 15.625 kHz |
| Color Subcarrier Frequency | 3.579545 MHz | 4.433618 MHz |
| Lines/Field | 525/60 | 625/50 |
NTSC vs PAL: Electrical power system
Transmission using different electrical power systems is the beginning of the differences between NTSC and PAL. In America and other countries that adopt the NTSC signal, electrical power is generated at 60 hertz. That means NTSC signal is transmitted at 60 'fields' per second (30 images are sent out per second). In Europe and other countries using the PAL signal, electricity supply is 50Hz, which means the PAL signal is sent out at 50 pulses per second (25 images per second).
NTSC vs PAL: Resolution quality
Another difference between NTSC and PAL is their resolution quality. PAL television contains 625 lines while NTSC has 525. Generally speaking, more lines means more visual info, namely, better picture quality and resolution. So when converting NTSC videos to PAL, usually some black bars are added to compensate for the smaller screen aspect. Usually, PAL files in a resolution of 720×576 pixels while NTSC in 720×480.
Above are the main differences between NTSC and PAL. To make a conclusion and put it simple, we can say the differences are:
1. NTSC is used in countries where electricity supply is in 60Hz while PAL is used in countries where electricity supply is 50Hz.
2. NTSC has a higher frame and image sending speed than PAL.
3. PAL has a higher resolution than NTSC, thus PAL image quality is better.
Countries that use NTSC vs. PAL
NTSC is used in Canada, Chile, Costa Rica, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Japan, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Peru, Philippines, Puerto Rico, South Korea, Taiwan and U.S.A. PAL is used in Afghanistan, Algeria, Argentina, Austria, Australia, Bangladesh, Belgium, Brazil, Bulgaria, China, Denmark, Finland, Germany, Hong Kong, Iceland, India, Indonesia, Iraq, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Jordan, Kenya, Kuwait, Liberia, Malaysia, Netherlands, Nigeria, Norway, New Guinea, Pakistan, Singapore, South Africa, South W. Africa, Sudan, Sweden, Switzerland, Thailand, Turkey, Uganda, United Kingdom, United Arab Emirates, Yugoslavia, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
Conversion from NTSC to PAL and vice versa
If a PAL movie is converted to an NTSC tape, 5 extra frames must be added per second or the action might seem jerky. The opposite is true for an NTSC movie converted to PAL. Five frames must be removed per second or the action may seem unnaturally slow.
